The concept of cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate in today’s digital age. With the increasing demand for flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, more and more companies are turning towards cloud computing solutions. Among the different types of cloud services available, public cloud stands out as one of the most popular options. In this article, we will delve into the world of public cloud and explore its various aspects, including its definition, features, benefits, use cases, and potential challenges.
What is Public Cloud?
Public cloud refers to a type of cloud computing service where IT resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, are made available to the general public over the internet by a third-party provider. In simpler terms, it is a shared pool of computing resources that can be accessed by multiple users simultaneously. These resources are scalable and available on-demand, meaning users only pay for what they use. Some of the leading public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
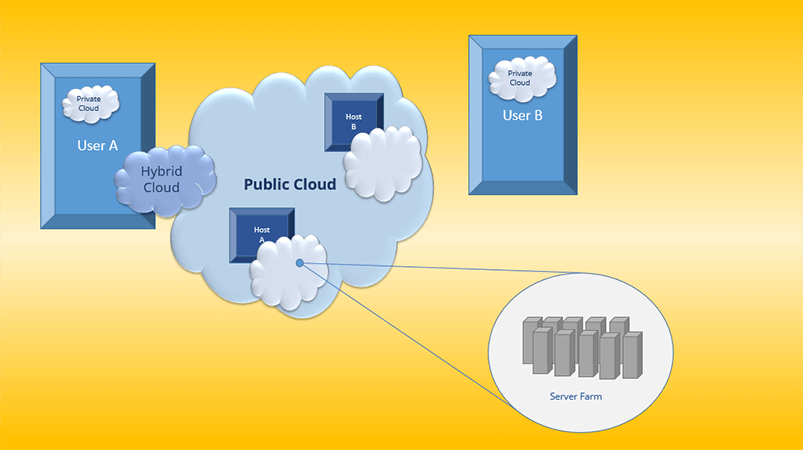
The public cloud denotes a form of cloud computing where IT resources are accessible to the public via the internet through a third-party provider
Characteristics of Public Cloud
- Multi-tenancy: Public cloud services are designed to cater to the needs of multiple users at the same time. This shared infrastructure model allows for better utilization of resources and cost savings for both the provider and users.
- Pay-per-use pricing: One of the key features of public cloud is its pay-per-use pricing model. This means that users only pay for the resources they consume, making it a cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes.
- Scalability: Public cloud offers the ability to easily scale up or down depending on the business needs. Users can quickly increase their resource allocation during peak periods and decrease it when the demand decreases, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Self-service provisioning: Most public cloud providers offer a self-service portal where users can provision and manage their services without any intervention from the provider. This empowers businesses to have more control over their resources, leading to increased efficiency.
- Security: Public cloud providers offer robust security measures to protect their infrastructure and data from cyber threats. However, it is also the responsibility of the user to implement additional security measures to safeguard their data.
- Accessibility: Public cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making it convenient for businesses with a distributed workforce or remote employees.
Benefits of Public Cloud
- Cost Savings: One of the most significant advantages of public cloud is its cost-effectiveness. With pay-per-use pricing and no upfront costs, businesses can save on hardware, software, and maintenance expenses.
- Scalability: As mentioned earlier, public cloud offers unmatched scalability compared to traditional on-premises solutions. Businesses can quickly scale up or down depending on their changing needs, eliminating the need for long-term commitments or overprovisioning.
- High Availability: Public cloud providers offer robust disaster recovery and high availability features, ensuring that businesses can access their resources even in case of a disaster or outage. This minimizes downtime and ensures business continuity.
- Flexibility: Public cloud offers flexibility in terms of resource allocation and management. Users can choose from a wide range of services and configurations based on their specific requirements, making it a versatile solution for all types of businesses.
- Innovation: With public cloud, businesses can take advantage of the latest technology and innovations without investing in expensive infrastructure. This enables companies to stay competitive and keep up with industry trends.
- Minimal Maintenance: Public cloud eliminates the need for businesses to maintain and upgrade their own hardware and software, saving them time and resources. The provider takes care of all maintenance and upgrades, allowing organizations to focus on their core competencies.

A major benefit of the public cloud is its cost-efficiency
Use Cases of Public Cloud
- Development and Testing: Public cloud is an ideal environment for software development and testing. It offers developers a cost-effective, scalable, and secure platform to build and test applications without investing in expensive infrastructure.
- Web Hosting: Many businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, use public cloud for web hosting. Public cloud providers offer easy-to-use tools and services to host websites and web applications, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to establish an online presence.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Public cloud offers affordable and reliable backup and disaster recovery solutions for businesses of all sizes. With high availability and data redundancy features, organizations can ensure the safety and accessibility of their data in case of a disaster or outage.
- Big Data Analytics: Public cloud provides businesses with the resources needed to analyze large volumes of data quickly and efficiently. This enables companies to gain insights and make data-driven decisions without investing in expensive hardware and software.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Many SaaS providers utilize public cloud services to host their applications and services. This allows them to offer their solutions to customers over the internet, eliminating the need for on-premises installations.
- Internet of Things (IoT): With the proliferation of IoT devices, businesses are turning towards public cloud to manage and process the vast amounts of data generated by these devices. Public cloud offers the scalability and processing power needed to handle IoT workloads effectively.
Challenges of Public Cloud
- Security Concerns: One of the biggest concerns surrounding public cloud is security. As data is stored and processed off-site, businesses have limited control over its security. However, most public cloud providers offer robust security measures and comply with industry standards and regulations to address these concerns.
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating from one public cloud provider to another can be complex and costly, leading to vendor lock-in. To avoid this, businesses can adopt a multi-cloud strategy, where they use services from multiple cloud providers.
- Internet Dependency: As public cloud services are accessed over the internet, businesses need a reliable and high-speed internet connection to ensure optimal performance. A poor internet connection can lead to slow response times and impact productivity.
- Limited Customization: Public cloud services may not offer the level of customization that some businesses require. This can be a challenge for organizations with unique or complex IT requirements.
- Compliance and Data Governance: Businesses operating in industries with strict compliance regulations, such as healthcare or finance, may face challenges when it comes to data governance and compliance in the public cloud. It is essential for these organizations to carefully select a provider that complies with all necessary regulations.
- Lack of Support: While most public cloud providers offer excellent customer support, some users may feel that the level of support received does not match their needs. This can be challenging for businesses that require hands-on support or have complex infrastructure.
How to Choose the Right Public Cloud Provider
Selecting the right public cloud provider is crucial for businesses looking to leverage its benefits. With numerous options available in the market, here are some factors to consider when choosing a public cloud provider:

Choosing the appropriate public cloud provider is essential for businesses aiming to utilize its advantages
Features and Services Offered
The first step in choosing a public cloud provider is to determine the business needs and the services required. Some providers may specialize in certain areas or offer a wider range of features and services. Businesses should thoroughly research and compare different providers to find the one that best meets their requirements.
Reliability and Uptime
Uptime refers to the percentage of time a service is available without any interruptions. It is essential for businesses to choose a public cloud provider with a proven track record of high uptime. This will ensure minimal disruption to their operations and maintain productivity.
Security Measures
As discussed earlier, security is a top concern when it comes to public cloud. Businesses should carefully assess the security measures and protocols of potential providers to ensure the safety of their data.
Pricing and Cost Structure
Pricing is a crucial factor for businesses looking to adopt public cloud services. While most providers offer a pay-per-use model, the pricing structure may vary based on the features, services, and resource usage. Organizations should carefully evaluate different pricing models and choose the one that aligns with their budget and needs.
Customer Support
In case of any issues or concerns, it is vital to have reliable customer support from the public cloud provider. Businesses should look for providers that offer 24/7 customer support and have a good track record of addressing and resolving customer queries.
Future of Public Cloud
The public cloud market is expected to continue its rapid growth in the coming years. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the public cloud market size is projected to reach $623.3 billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 29% during the forecast period. With the increasing demand for digital transformation, businesses are likely to adopt public cloud solutions to stay competitive and meet customer expectations.
Some emerging trends in the public cloud space include:
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing allows businesses to run applications without worrying about server management. This trend is gaining popularity in the public cloud space, as it offers cost savings and simplified infrastructure management.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing and analyzing data closer to the source rather than sending it to the cloud. This trend is expected to gain traction as it reduces latency and improves application performance.
- Hybrid and Multi-cloud: As mentioned earlier, vendor lock-in is a significant challenge for organizations using public cloud services. To address this, more businesses are adopting a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy, where they use services from multiple providers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is finding its way into public cloud services, enabling businesses to leverage the power of AI without investing in expensive infrastructure. This trend is expected to continue as more organizations look to incorporate AI into their operations.
Conclusion
The rise of public cloud has transformed the IT landscape and how businesses operate. Its ability to provide on-demand, scalable, and cost-effective resources makes it an attractive option for companies of all sizes. With its features and benefits, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital world. However, choosing the right public cloud provider and addressing potential challenges are crucial for successfully adopting this technology. With its continued growth and evolving trends, public cloud is set to play a significant role in shaping the future of businesses.



