In today’s digital age, data is the driving force behind many industries. From business analytics to consumer trends, data has become the backbone of decision making. However, with the ever-growing amount of data being produced, the traditional method of centralized cloud computing faces challenges in terms of speed, scalability and cost. As a solution, edge computing has emerged as a game-changer in the world of data processing. In this article, we will delve into the concept of edge computing, its benefits, applications, challenges and future prospects.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing refers to the decentralized approach of data processing, where the computation takes place closer to the source of data generation instead of a centralized cloud server. This means that data is processed at the “edge” of the network, i.e. on devices or servers located closer to the end-users or data sources. The concept of edge computing was first introduced by Cisco in 2014 and has gained significant traction in recent years.
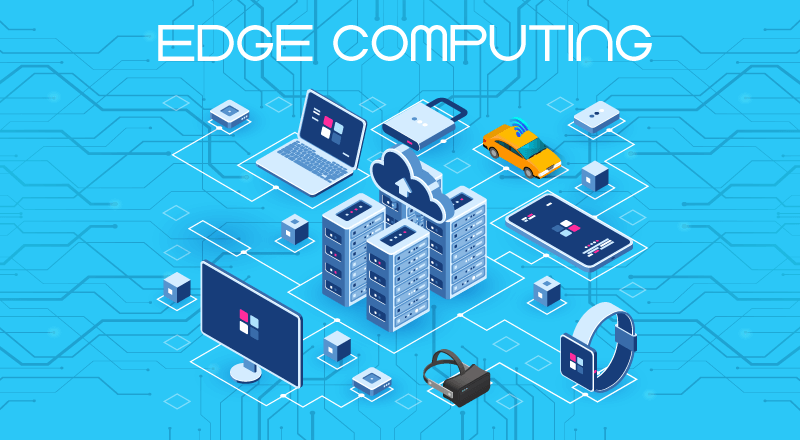
Edge computing involves processing data closer to its origin rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers for computation
Definition and Explanation
In simple terms, edge computing can be defined as “computing at the edge of the network.” It aims to bring processing power closer to where data is being generated, rather than sending it to a central server for analysis. This allows for faster processing, reduced latency, and improved bandwidth utilization.
To understand edge computing better, let’s compare it with traditional cloud computing. In traditional cloud computing, data is sent to a centralized server, also known as the cloud, for storage, processing and analysis. This means that all requests for data processing are routed through a single point, leading to potential delays and slower response times. In contrast, edge computing utilizes a distributed architecture where computation takes place on devices or servers located at the “edge” of the network. This approach reduces the distance between the source of data and the processing unit, resulting in faster data processing.
Comparison with Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has been the preferred method for data storage and processing for the past decade. However, with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and other technology advancements, the limitations of cloud computing have become evident. One of the major drawbacks of cloud computing is latency, i.e. the time taken for data to travel from a device to the cloud and back. This delay can cause significant issues in applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation. On the other hand, edge computing offers faster processing and reduced latency by bringing computation closer to the data source.
Another aspect where edge computing excels is scalability. In cloud computing, the cost of adding more servers or storage capacity can be high, making it challenging for smaller companies to scale up their operations. Edge computing allows for a more cost-effective and modular approach to scaling, as additional processing units can be added as needed, without relying on a central server.
Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers several advantages over traditional cloud computing, making it an attractive option for businesses and industries alike.

Edge computing provides numerous benefits compared to conventional cloud computing
Real-time Data Processing
One of the primary benefits of edge computing is its ability to process data in real-time. With the increasing use of IoT devices, there is a growing demand for real-time data processing in applications such as smart homes and cities, healthcare, and industrial IoT. Edge computing enables quick analysis and response to data, allowing for faster decision-making and improved user experience.
Reduced Latency
As mentioned earlier, latency can be a significant issue in cloud computing, especially for applications that require immediate responses. In edge computing, data is processed closer to the source, resulting in reduced latency. This is particularly crucial in time-sensitive situations, such as autonomous vehicles where even a slight delay can have severe consequences.
Improved Bandwidth
Edge computing also helps in improving bandwidth utilization by reducing the amount of data sent to the cloud for processing. With the growth of data-intensive applications, the strain on networks and servers has increased, leading to slower response times. By processing data at the edge, only relevant information is transmitted to the cloud, resulting in efficient bandwidth usage.
Cost-effectiveness
Edge computing offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional cloud computing. As data is processed at the edge, there is less reliance on a central server, reducing infrastructure costs. Moreover, with the modular approach to scalability, businesses can add processing units as needed, without significant upfront investments.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
In edge computing, data is not transferred to a centralized server, reducing the risk of potential security breaches. This is especially important in sensitive industries such as healthcare, where privacy and security are paramount. Edge computing also allows for local storage and processing of data, making it harder for hackers to access sensitive information.
Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing has a wide range of applications, with its potential seen in various industries.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT market is growing exponentially, with an estimated 31 billion connected devices by 2025. With the rapid growth of IoT, edge computing has emerged as a critical component in processing the massive amounts of data generated by these devices.
Smart Homes and Cities
Edge computing enables faster and more efficient processing of data in smart homes and cities. From controlling home appliances to managing traffic signals, edge computing can process data in real-time, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced congestion.
Industrial IoT
In industrial IoT, edge computing plays a crucial role in automation and predictive maintenance. By analyzing data in real-time, edge computing helps in identifying potential issues before they occur, reducing downtime and costs for businesses.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, edge computing is transforming patient care and management. With the rise of wearable devices and remote patient monitoring systems, edge computing enables quick analysis and response to vital signs, allowing for timely interventions and improved treatment outcomes.
Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing is a critical component in the development of autonomous vehicles. By processing data in real-time, edge computing helps in navigation, object recognition, and decision-making, making autonomous driving safer and more efficient.
Augmented and Virtual Reality
The seamless experience of augmented and virtual reality applications heavily relies on low latency and high bandwidth. Edge computing makes this possible by enabling quick processing of data, resulting in a more immersive and responsive experience.
Challenges in Implementing Edge Computing
While edge computing offers numerous benefits, there are still challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption.
Although edge computing presents many advantages, there remain obstacles that must be overcome for it to be widely adopted
Hardware Limitations
One of the primary limitations of edge computing is the hardware required for processing data at the edge. As the size of data sets increases, so does the need for more powerful processors and storage units. This poses a challenge for smaller businesses or organizations with limited resources.
Network Connectivity
Edge computing relies on a robust and reliable network infrastructure for quick data processing. However, in areas with limited connectivity or weak networks, the effectiveness of edge computing may be hindered. This is especially relevant in industrial settings where connected devices may be located in remote locations.
Data Management
As data is processed at various points on the edge, managing and synchronizing this data can be a challenge. Standardization of data formats and protocols is crucial for efficient data management in edge computing. Without proper synchronization, there may be discrepancies in data, leading to inaccurate analysis and decision-making.
Standardization
The lack of standardization in edge computing is another significant challenge. With different manufacturers producing their own edge devices and software, interoperability can become an issue. This can lead to compatibility issues and make it difficult for businesses to integrate edge computing into their existing systems.
Future Prospects of Edge Computing
The market for edge computing is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global edge computing market is projected to reach USD 15.7 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 25.4%. Technological advancements such as 5G networks, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are expected to fuel the growth of edge computing. These technologies will enable faster processing and analysis of data, making edge computing even more efficient and effective.
With the rise of edge computing, we can expect to see its impact on various industries. In manufacturing, edge computing can help optimize supply chain management and improve efficiency. In retail, it can enable real-time monitoring of inventory and customer behavior. The healthcare sector is expected to see significant benefits from edge computing, with improved patient care and management. Moreover, with the increasing use of IoT devices and autonomous vehicles, the demand for edge computing will only continue to grow.
Conclusion
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way we process and manage data. Its benefits in terms of real-time processing, reduced latency, and cost-effectiveness make it a game-changer in the world of technology. While there are challenges that need to be addressed, the future of edge computing looks promising, with its potential seen in various industries. As we move towards a more connected and data-driven world, edge computing will play a crucial role in improving efficiency, enhancing user experience, and driving innovation.